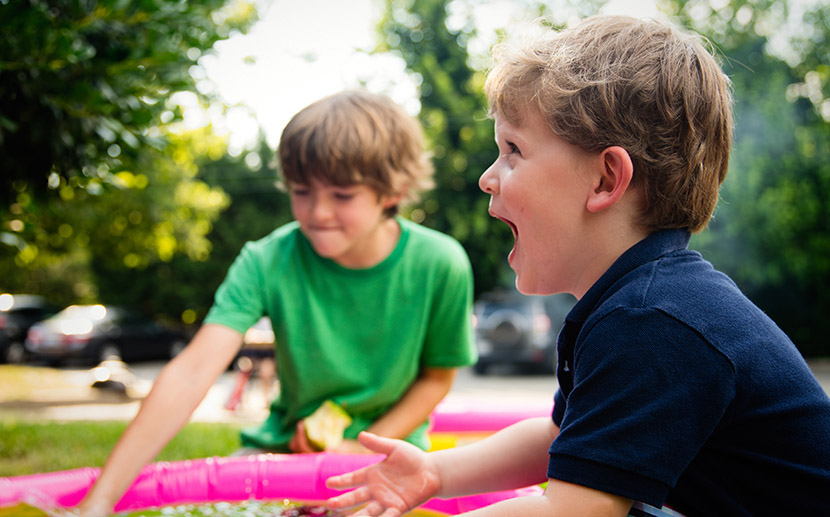
What is Stuttering?
Stuttering is a difficulty in the flow of speech. Although the type and amount of dysrhythmias differ from person to person, the following features are usually common.
A person who stutters can present in his speech:
- Repeat entire words (eg, the, the, the, the boy)
- Repeat words sections (eg with … with … with … after)
- Sound extensions (for example, the oooooooother was)
- Blocks of sounds, where the mouth holds a steady position without the sound coming out
- Intensity on face
- Fluctuations in the respiratory system (steep inhalation, breathing, etc.)
- Total body movements
People with stuttering are not lagging behind the rest simply have difficulty saying what they want. The repetition of sounds, gestures or even words, blocking the flow of the tongue are some stuttering symptoms that are readily perceived by the social environment and have positive (direct interference) or negative (laughter, fear) effects on individuals.
Speaking Too Fast
Speaking faster than the normal is a disorder of the flow of speech. In the tachylae the joint is not clear – clean. Speech has a fast pace. Words are pronounced rushed, falsified and all of this results in speech not being fully understood and communication difficult.
In addition, the following phenomenon is observed: while the thought runs at a fast pace, speech can not follow it at this rate. In other words, thought does not advance in words, which results in the appearance of this disorder.
However, the effects of speaking too fast on the individual are not limited to reciting – a proposal. They are often extended to the written language, which may present an infrequent written word with letters omissions and word falsification.
The articulation and vocalization also present deviations, and in particular during the speech we have frequent inhalations and messy rhythm in the words spoken and between the words voids.
Symptoms:
- Speeding up big word and suggestion. Large words and sentences are not pronounced whole, because the pace of speech is fast and on the other hand because it is trying to find the right words.
- Acceleration in pronunciation leads to the omission of syllables or their repetition, resulting in the appearance of features observed in stuttering.
- Limited use of consonants and fake pronunciation of phonograms. The reason is so short, there is no time for complex joints. Thus, we are leading to syllable parallels, to known fragments.